-
Product
-
Fiber laser cutting machine
-
Profile Steel/ H-Beam Laser Cutter
high efficiency | high-performance | high quality -
Full Cover Fiber Laser Cutting Machine
supreme configuration | high precision | safe & pollution-free -
Sheet fiber laser cutting machine
tailor-made machine | efficiency boost -
Fiber Laser Bevel Cutting Machine
one-shot bevel | efficiency boost | streamlined process -
High precision fiber laser cutting machine
High precision | small footprint | fully enclosed -
Four-chuck Tube Cutting Lasers
truly zero-tailing | low cost per part | auto loader -
Three-chuck Tube Laser Cutting Machine
top production output | low cost per part | extremely short tailing -
Two-chuck Tube Laser Cutting Machine
top production output | low cost per part | extremely short tailing -
Full Enclosed Fiber Laser Cutting Machine
Integrated design saves installation time and shipping costs. - flexible processing | continuous cutting | efficient production
-
Fully Automatic Loading & Unloading Laser Cutting Production Line
intelligent production | optimizing factory space | reduce labor costs -
Sheet and Tube Fiber Laser Cutting Machine
supreme cost-effectiveness | dual-use laser | space-saving
-
-
Fiber laser welding machine
-
Air-cooled Portable Laser Welding Machine
more flexibility | easy to use | cost effective -
Automatic laser welding machine
fine welding seam | boosted efficiency -
Integrated fiber laser welding machine
instant welding | easy to operate & move -
Handheld fiber laser welding machine
long distance welding | multi-welding modes
-
- Fiber laser cleaning machine
- Bending Machine
-
Fiber laser cutting machine
- Solutions
- Why Morn Laser
- Price
- Contact
- VR
Menu
X- home
-
Product >
-
Laser Cutting vs Plasma Cutting: Which One Is Right for Your Metal Fabrication Business?
2025-07-11When it comes to cutting metal, both laser cutting and plasma cutting are widely used technologies in modern fabrication. However, they differ significantly in terms of cutting quality, speed, precision, and cost.
Understanding the key differences between laser and plasma cutting can help you choose the right process for your specific application—and ensure better long-term performance, efficiency, and return on investment.
How Each Technology Works
Laser cutting uses a highly focused beam of light—typically from a fiber laser source—to melt or vaporize material with extreme precision. It's a non-contact process, guided by CNC controls and ideal for both thin and thick metals.
Plasma cutting, on the other hand, relies on a high-temperature jet of ionized gas (plasma) to melt the material. It requires electrical conductivity in the material and is most commonly used for cutting thicker metals in industrial settings.
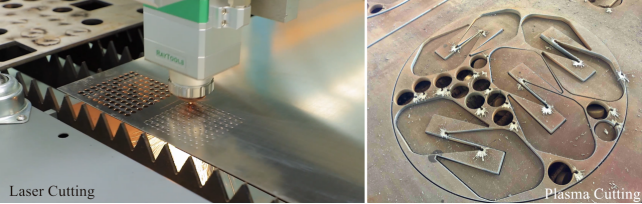
Key Differences Between Laser Cutting and Plasma Cutting
1. Cutting Precision and Edge Quality
Fiber laser cutter offers a finer kerf, tighter tolerances, and smoother edges.
Plasma cutting generally produces wider kerfs and more dross (slag), especially on thinner materials, often requiring grinding or secondary finishing.
2. Material Thickness and Compatibility
Laser cutting excels at cutting thin to thick metals such as stainless steel, carbon steel, aluminum, and brass—typically up to 150–180mm with high-power fiber lasers.
Plasma cutting is more commonly used for thicker metals, especially carbon steel plates over 30 mm, but is less suitable for non-ferrous or highly reflective materials like aluminum or copper at thin gauges.
3. Cutting Speed
Fiber laser cutting machine is generally faster and more efficient.
4. Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ)
Laser cutting has a smaller heat-affected zone, reducing the risk of warping and maintaining material strength near the cut. Plasma cutting, with higher thermal input, can distort delicate parts or create larger HAZs.
5. Operating Costs
Plasma systems typically have lower upfront costs but higher long-term operating costs due to consumables (electrodes, nozzles), gas usage, and lower energy efficiency.
Fiber laser cutters may require a higher initial investment, but their low maintenance, minimal consumables, and higher energy efficiency often result in a better total cost of ownership over time.
6. Automation and CNC Integration
Laser cutters are easier to integrate into automated production lines. Features like autofocus heads, nesting software, and real-time monitoring make them well-suited for Industry 4.0 manufacturing.
While plasma systems can also be CNC-controlled, they are typically less precise and less optimized for automation-driven workflows.

Which One Should You Choose?
Laser cutting is the better choice if your application requires:
High precision and fine detail
Minimal post-processing
Cutting thin to medium-thick sheet metal
Low scrap and better material utilization
Compatibility with automation
Plasma cutting may be more suitable if:
You primarily work with very thick steel (40 mm and above)
You have lower accuracy requirements
Your budget is limited and post-processing is acceptable
Why More Manufacturers Are Choosing Laser Cutting in 2025
With the evolution of high-power fiber lasers (12kW–80kW), the gap between laser and plasma cutting is narrowing—even for thick materials.
Metal laser cutters now offer:
Faster processing of mild steel up to 120 mm
Cleaner bevel cutting and hole quality
Lower labor and consumable costs
Full compatibility with smart factories
As a result, more companies are transitioning to laser cutting—not just for quality, but for long-term scalability and automation readiness.
At Morn Laser, we provide advanced fiber laser cutting solutions from 1kW to 80kW, suitable for thin sheet cutting, thick plate processing, and fully automated workflows.
- Office Address:
- 17F, Building 5, Qisheng Mansion High-Tech Zone, Jinan, Shandong 250101, China
- Email: info@mornlaser.com
- Mobile/WhatsApp/WeChat: +86 151 6916 6350
CONTACT USCopyright © 2008-2022 Morn Laser All Rights Reserved.![]() Get a Quote
Get a Quote
![]() Get a Quote
Get a Quote
Cookies
We use cookies to improve our services and remember your choice for future visits. By clicking "Accept cookies", you consent to the use of cookies on this website.
Read our Privacy Policy
Get a Quote x
![]()